Small RNA NGS Solutions
Related Products
Related Services
Related Reviews
snoRNA Sequencing Service
Arraystar snoRNA sequencing service offers sample-to-data snoRNA (60–300 nt size range) expression profiling solution. With the wealth of snoRNA-seq information, investigators are empowered to advance their next step research in this field of study.
Note: For profiling snoRNA-derived fragments (sdRNAs, 16~36 nt size range), a regulatory small RNA class related to but size-distinct from snoRNA, please use sdRNA analysis package covered under Arraystar tRF & tiRNA Sequencing Service data (14~40 nt size range).
Benefits:
- Performance optimized snoRNA sequencing method with rigorous QC process
- 60–300 nt snoRNA size range selection by gel electrophoresis for comprehensive snoRNA coverage
- Detailed snoRNA annotation and authoritative classification based on Ensembl reference.
- Publication quality graphics and data visualization.
Promo.: 30% OFF. Valid through 1/31/2026.
| Service Name | Price |
|---|---|
| snoRNA Sequencing Service |
Small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) are 60~300 nt, evolutionarily conserved small non-coding RNAs enriched in the nucleolus. snoRNAs can be classified into C/D box (SNORD) snoRNAs and H/ACA box (SNORA) snoRNAs that direct 2′-O-methylation and pseudouridylation of rRNAs, snRNAs and tRNAs, respectively. snoRNAs also aid pre-rRNA cleavage and, in some cases, mRNA splicing or 3′-end maturation. When packaged into extracellular vesicles, snoRNAs may mediate intercellular communication[1].
snoRNAs can be processed into snoRNA-derived small RNA fragments (sdRNAs) that may function similarly to miRNAs or piRNAs[1].
Recent studies have redefined snoRNAs as multifunctional regulators in addition to RNA modification: they act as protein-scaffolding platforms in gametogenesis [2], control ribosome assembly and p53-driven cell senescence via direct RPL23 interaction [3] (Fig. 1), direct secretory mRNAs to the signal recognition particle (SRP) machinery through ternary RNA gluing [4] (Fig. 2), reprogram chromatin by disrupting PRC2 to derepress ESM1 in fibroblast-like synoviocytes of Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) [5], and ameliorate differentiation defects in myotonic dystrophy[6]. Collectively, these findings establish snoRNAs as versatile trans-acting organizers of gene expression, protein trafficking, and cell fate that operate beyond their canonical rRNA-guided roles.
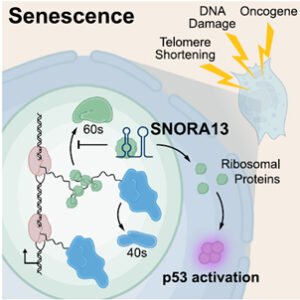
Figure 1. snoRNA drives p53-mediated cell senescence by blocking ribosomal protein uptake into nascent subunits[3].
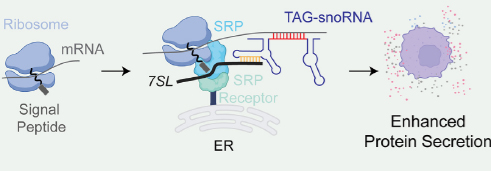
Figure 2. snoRNA functions as a “molecular glue” that connects secretory protein mRNAs to the signal recognition particle (SRP) complex through novel ternary RNA interactions[4].
Dysregulated snoRNAs can act as oncogenes or tumor suppressors in cancers[7], mediate cancer treatment resistance[8] (Fig. 3), contribute to cardiovascular disorders such as hypertrophic/dilated cardiomyopathy and myocardial infarction (Fig. 4); play roles in neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Huntington’s), Prader-Willi syndrome, and leukoencephalopathy [7, 9] (Fig. 5). Due to their stability in biofluids, tissue specificity, and disease correlation, snoRNAs hold strong potential as non-invasive biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
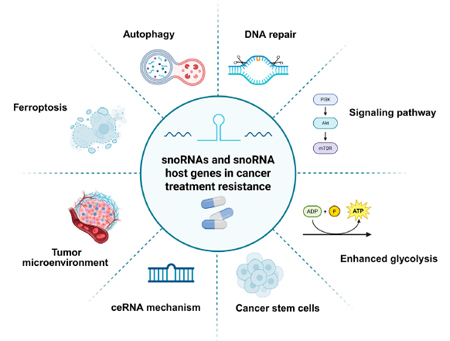
Figure 3. snoRNA contribute to cancer treatment resistance[8].
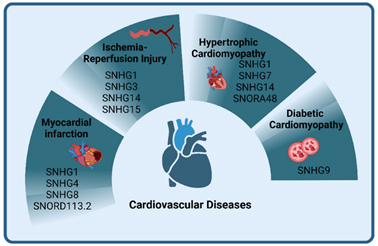
Figure 4. snoRNA contribute to cardiovascular diseases[9].
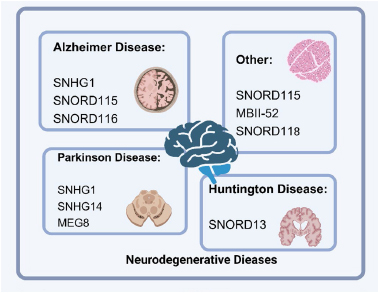
Figure 5. snoRNAs play roles in neurodegenerative diseases [7].
References
[1] Jouravleva K, Zamore PD: A guide to the biogenesis and functions of endogenous small non-coding RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2025, 26(5):347-370.[PMID: 39856370]
[2] Leroy E et al: A bifunctional snoRNA with separable activities in guiding rRNA 2′-O-methylation and scaffolding gametogenesis effectors. Nat Commun 2025, 16(1):3250.[PMID: 40185772]
[3] Cheng Y et al: A non-canonical role for a small nucleolar RNA in ribosome biogenesis and senescence. Cell 2024, 187(17):4770-4789 e4723.[PMID: 38981482]
[4] Liu B et al: snoRNA-facilitated protein secretion revealed by transcriptome-wide snoRNA target identification. Cell 2025, 188(2):465-483 e422.[PMID: 39579764]
[5] Huang J et al: snoRNA Snord3 promotes rheumatoid arthritis by epigenetic regulation of ESM1 in fibroblast-like synoviocytes in mice. Sci Transl Med 2025, 17(824):eadt5340.[PMID: 41223251]
[6] Bogard B et al: Small nucleolar RNAs promote the restoration of muscle differentiation defects in cells from myotonic dystrophy type 1. Nucleic Acids Res 2025, 53(6).[PMID: 40156865]
[7] Li Y et al: Unlocking the life code: a review of SnoRNA functional diversity and disease relevance. Cell Commun Signal 2025, 23(1):266.[PMID: 40468441]
[8] Yan X et al: Mechanisms of snoRNAs in cancer treatment resistance: from molecular insights to clinical applications. Trends Genet 2025, 41(12):1144-1157.[PMID: 40651850]
[9] Chabronova A et al: SnoRNAs in cardiovascular development, function, and disease. Trends Mol Med 2024, 30(6):562-578.[PMID: 38523014]
The snoRNA-seq provides rich bioinformatics analyses to better understand their biology and facilitate biomarker applications.
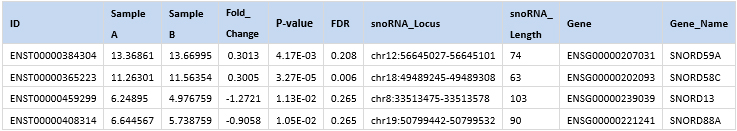
Figure 1. A snapshot of differentially expressed snoRNAs.
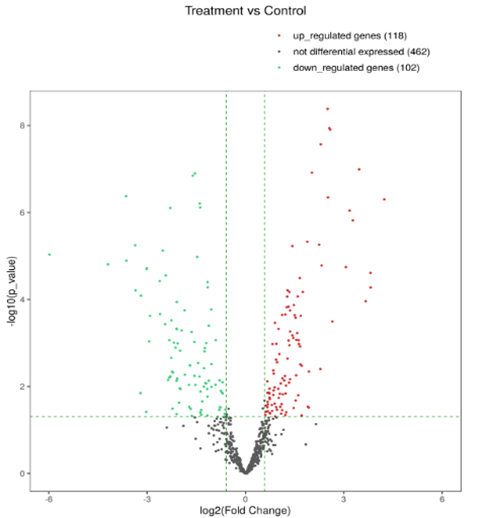
Figure 2. Volcano plot of up- (red) and down-(green) regulated snoRNAs, indicating fold change (horizontal axis) and statistical significance (vertical axis).
