|
|
| Why and how to study epigenetic regulations by R-loops? |
|
Often located in the CpG islands of the promoters or transcription stop sites, R-loops have important biological functions in epigenetic and transcriptional regulation. Let’s look at the impact on epigenetic regulation first.
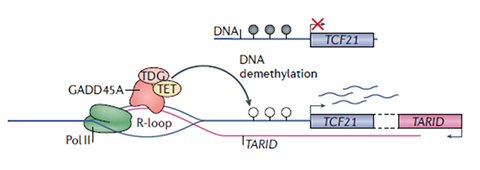
DNA methylation regulation by R- loops Figure 1. R-loop with antisense lncRNA TARID binds GADD45A, recruits TET1 to the CpG island of TCF21 gene promoter, demethylates the DNA, and activates the TCF21 transcription [4]. This R-loop mechanism via gene methylation can be studied by DRIP-seq, along with LncRNA Array and MeDIP-seq. Chromatin remodeling by R-loop This mechanism via chromatin remodeling can be studied by DRIP-seq along with LncRNA Array and ChIP-seq. |
| Learn More About R-loops | DRIP-seq Service |
|
1. Nadel J. et al (2015) Epigenetics Chromatin 8:46 [PMID:26579211] 2. Ginno PA. et al (2012) Mol Cell 45(6):814-25 [PMID:22387027] 3. Grunseich C. et al (2018) Mol Cell 69(3):426-437.e7 [PMID:29395064] 4. Arab K. et al (2019) Nat Genet 51(2):217-223 [PMID:30617255] 5. Beckedorff FC. et al (2013) PLoS Genet 9(8):e1003705 [PMID:23990798] 6. Wang X. et al (2008) Nature 454(7200):126-30 [PMID:18509338] |
|