|
Small RNAs, including microRNAs and tRNA-derived small RNAs (tsRNAs), harbor a diversity of RNA modifications. The modifications, such as 5-methylcytidine, 7-methylguanosine, 8-oxoguanine, pseudouridine and m6A-methylation modulate the activities of small RNAs in diverse biological processes and play pivotal roles in pathological conditions.
|
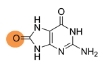
8-oxoguanine (o8G)
o8G modification in the seed region (positions 2–8) of miRNAs alters the mRNA targeting and target specificity, having profound biological consequences. Learn more>>
|
|
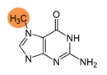
7-methylguanosine (m7G)
m7G methyltransferase METTL1 binds directly to miRNA precursors and installs m7G, thus accelerating pre-miRNA processing. After processing, the m7G may still remain and modulate the mature miRNA function.
Learn more>>
|
|
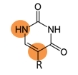
Pseudouridine (Ψ)
Catalyzed by pseudouridine synthase 7 (PUS7), pseudouridylation in the 5’-terminal oligoguanine (TOG) of tsRNA can activate global tsRNA-mediated translation inhibition in human embryonic stem cells.
Learn more>>
|
|
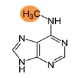
m6A-methylation (m6A)
m6A modification affects miRNA functions. m6A methylation in miRNAs is significantly increased in cancers and can be a diagnostic biomarker for early-stage cancer detection. Learn more>>
|
|
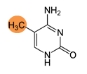
5-methylcytidine (m5C)
m5C causes structural changes in the RISC complex. m5C in miRNAs also disrupts the formation of miRNA/mRNA duplex, and leads to the loss of gene silencing activity. Learn more>>
|
Arraystar Small RNA Modification Array Service is designed to quantify o8G, m7G, m6A, Ψ, or m5C modifications in miRNAs, pre-miRNAs, and tsRNAs on a single array, providing the key information to study regulatory impacts of the small RNA modifications.
|
To start your research on small RNA modifications
|
|
|
|
To learn more on small RNA modifications:
• Small RNA Modifications: Integral to Functions and Diseases
• Molecular Mechanisms of Small RNA Modifications
• The Challenges and Solutions of Studying Modified Small RNAs
|
|
|





